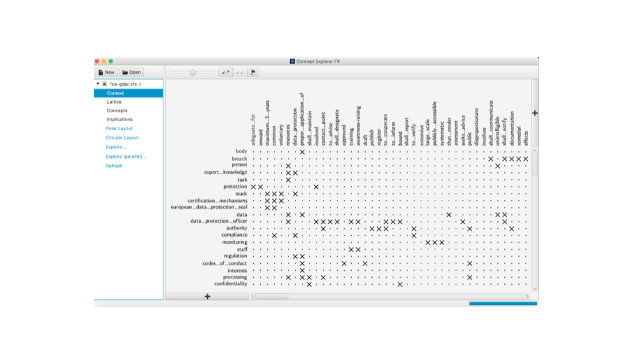
1. What software design principles enable GDPR-compliance by-design?
"Research question 1 is aimed at distilling any widely applicable laws, guidelines,biases and design considerations reflecting the accumulated knowldge and experience garnered through FCA analysis of the regulation; examples of similar design principles are the SOLID object-oriented design principles."